UAE Sustainability Initiatives
Federal Initiatives

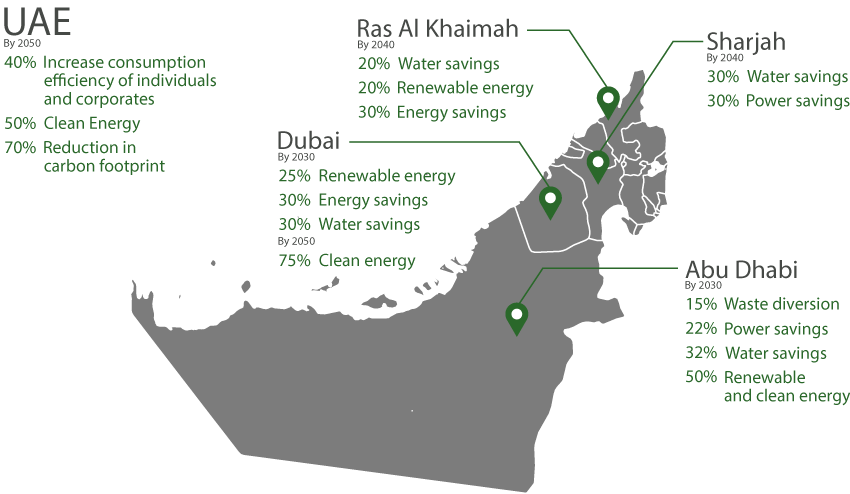
Vision 2050
UAE Energy Strategy 2050:
The UAE Energy Strategy 2050, was announced by Vice President and Prime Minister of the UAE and Ruler of Dubai H.H. Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum in November 2015 and updated in 2024, aims to transition to a sustainable energy mix. By 2030, it targets a 30% share of clean energy, a 42-45% improvement in energy efficiency, and an increase in clean energy capacity to 19.8 GW. The strategy seeks to triple renewable energy contribution, create 50,000 green jobs, and achieve AED 100 billion in savings. By 2050, it envisions net-zero emissions in the energy and water sectors.
Green Finance for Sustainable Development in the UAE
Sustainable finance plays a pivotal role in shaping a greener and more resilient built environment. By channelling investments into environmentally responsible projects, sustainable finance supports innovative solutions that reduce carbon emissions, enhance energy efficiency, and promote resource conservation in buildings and infrastructure. From green bonds to sustainability-linked loans, financial mechanisms are driving the transition to a low-carbon economy and enabling the integration of sustainability principles in every stage of the building lifecycle.
During COP28, the Central Bank of the UAE announced a commitment of AED 1 trillion in sustainable finance by 2030, to support energy-efficient building projects, retrofitting existing infrastructure, and integrating renewable energy, to ensure that projects in the built environment incorporate resilience against climate risks.
Read more about sustainable finance in the Central Bank of the UAE Annual Report.
Abu Dhabi Initiatives

Abu Dhabi Climate Change Strategy
Abu Dhabi is to deliver a 22% reduction in carbon emissions by 2027, equivalent to the sequestration by 500 million trees over the period of 10 years, supporting the UAE Net Zero by 2050 strategic initiative. The Abu Dhabi Climate Change Strategy is to focus on two pillars, first, mitigation, which ensures economic growth while reducing climate emissions. Through decarbonization and innovative technologies, incentivising sustainability, and major renewable energy production projects, mitigation will be achieved, and greenhouse gas emissions will be reduced. The second pillar is adaptation, which focuses to enhancing the resilience and agility of key economic sectors, such as energy, health, infrastructure, and the environment, against climate risks.
Looking into achieving the objectives set, the Abu Dhabi Climate Change Strategy will implement 81 initiatives and 12 key strategic projects, including low-emissions vehicles, mangrove restoration, green procurement, Al Dhafra PV (Solar) Plant. Looking into Abu Dhabi’s key climate action milestones so far, one milestone noteworthy mentioning is that the Emirates Water and Electricity Company meets 80% of total power demand through renewable and clean energy from solar and nuclear energy plants
To support the UAE Energy Strategy 2050, the emirate of Abu Dhabi has identified key focus areas to improving the energy sector:
The five priority areas of the Abu Dhabi Environment Vision 2030 are:
- Renewable Energy
- Clean Alternative Fuels
- Energy Storage
- Carbon Capture and Storage
- Energy Efficient Technologies
Environment Vision 2030
Environment Vision 2030 was developed by Environment Agency – Abu Dhabi (EAD) in close coordination with the General Secretariat of the Executive Council and Department of Economic Development / Abu Dhabi Council for Economic Development, to ensure integration among the three pillars of sustainability: environment, economic, and social vision
The five priority areas of the Abu Dhabi Environment Vision 2030 are:
- Climate Change
- Clean Air and Noise Pollution
- Water Resources
- Biodiversity, Habitats and Cultural Heritage
- Waste Management
Click here to read more about the Abu Dhabi’s Environment Vision 2030.
Estidama Pearl Rating System
Following the launch of the Estidama framework in 2008, the Department of Urban Planning and Municipalities (DPM) – formerly known as Abu Dhabi Urban Planning Council (UPC) – developed the Estidama Pearl Rating System (PRS) in 2010, addressing four pillars of sustainability: environmental, economic, social and cultural. The PRS is mandatory for all new buildings in the Abu Dhabi Emirate. It is also the first mandated sustainability rating system in the Arab region.
Dubai Initiatives

Dubai Integrated Energy Strategy 2030
The Dubai Supreme Council of Energy has formulated and launched the Dubai Integrated Energy Strategy 2030 in 2011, with the purpose of diversifying sources of energy and increase the clean energy share. Dubai aims to increase the share of clean energy to 29% and the Emirate’s energy demand by 30% by 2030. Click here to learn more about the Dubai energy targets.
Dubai Clean Energy Strategy 2050
HH Sheikh Mohammad Bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Vice President and Prime Minister of the UAE and Ruler of Dubai, launched the Dubai Clean Energy Strategy 2050 in November 2015, which aims to make Dubai a global centre of clean energy and green economy. It aims to provide 75 % of the Emirate’s energy through clean energy sources by 2050. Click here to read more.
Dubai Green Building Regulations and Specifications and Al Sa’fat Rating System
Aligned with Dubai government’s strategic plans, Dubai Municipality launched its Green Building Regulations and Specifications (GBR&S) in 2011 to be applied as mandatory requireAligned with Dubai government’s strategic plans, Dubai Municipality launched its Green Building Regulations and Specifications (GBR&S) in 2011 to be applied as mandatory requirements for new construction in the Emirate. These regulations have been mandated on government owned buildings since 2011 and on all new buildings in Dubai starting 2014. Based on the GBR&S, Dubai Municipality introduced Al Sa’fat rating system in 2016 to strengthen the sustainable built environment in the city, and support the goal of Dubai’s Plan 2021 to create a smart and sustainable city. Click here to learn more about Al Sa’fat Rating System.ments for new construction in the Emirate. These regulations have been mandated on government owned buildings since 2011 and on all new buildings in Dubai starting 2014. Based on the GBR&S, Dubai Municipality introduced Al Sa’fat rating system in 2016 to strengthen the sustainable built environment in the city, and support the goal of Dubai’s Plan 2021 to create a smart and sustainable city. Click here to learn more about Al Sa’fat Rating System.
Trakhees EHS Regulations and Standards
Trakhees serves as a regulatory arm for the issuance of building permits, commercial licensing, and for the supervision of engineering and all health, environmental and safety related matters within the Free Zone. Trakhees has incorporated several sustainability credits into its own building assessment system. Click here to learn more about the Trakhees Regulations.
Ras Al Khaimah Initiatives
Ras Al Khaimah Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Strategy 2040
- Barjeel Green Building Regulations
- Building Retrofits
- Energy Management
- Efficient Appliances
- Efficient Street Lighting
- Water Reuse and Efficient Irrigation
- Solar Programs
- Energy from Waste
- Efficient Vehicles
To find out more, please visit the RAK Reem webpage.
Barjeel – Ras Al Khaimah Green Building Regulations
For more information about Barjeel, please visit the RAK Municipality website here.
Sharjah Initiatives
The Emirates of Sharjah is aligning its efforts and targets with the larger UAE 2050 Energy Strategy. The Sharjah Department of Public Works was established to take on civil construction in Sharjah to the highest quality standards. The vision of the Public Works of Sharjah is to have sustainable urban development.
The Sharjah Department of Public Works has highlighted numerous initiatives across multiple press releases, showcasing the progress made in sustainability within the emirate. The key focus areas inferred from these announcements include:
- Water
- Sustainable Buildings
- Building Retrofit
- Research and Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Renewable Energy
Know more about the Sharjah Department of Public Works here. In support of its above efforts, the Sharjah Department of Public Works developed the “Guide to Green Building”. The booklet was published in 2023, and has a chapter dedicated for Sustainable Building Standards, which covers topics such as environmental planning after construction, outdoor sustainable spaces, green walls, local vegetation, storm water management, high performance envelopes, shading devices, lighting control, renewable energy and several more topics.
Read more about the Guide to Green Buildings by the Sharjah Department of Public Works here.
Moreover, the Sharjah City Municipality developed the Booklet on Building Sustainability Specifications in the City of Sharjah. The booklet has nine chapters and covers different topics including, for example, materials and resources, Energy Use Efficiency, and Site Sustainability and Transport.
Ajman Initiatives
The Emirate of Ajman is dedicated to the UAE’s 2050 Energy Strategy through the Ajman Carbon Neutrality Path, which was unveiled at COP28. This initiative focuses on retrofitting the city’s existing buildings, which make up 70% of its area. Initially, the program will target industrial facilities, with plans to extend to business and government institutions, ensuring the achievement of carbon neutrality by 2050.
The initiative adopts several green practices, including the use of clean energy for the generation of electricity, waste management, sustainable transportation, and sustainable production system.
Read more about the Municipality and Planning Department of the city of Ajman.
The Municipality of Ajman also issued their Second Sustainability Report of 2019-2021, which covers several topics related to sustainability of the built environment, such as Quality Infrastructures and Roads and Workplace Health and Safety.
Umm Al Quwain Initiatives
Umm Al Quwain is advancing its sustainability efforts through a comprehensive approach, including a focus on a Sustainable Blue Economy, enhancing renewable energy use, and promoting environmental conservation. Through strategic collaborations, such as those announced at COP28, the emirate is taking significant steps to align with the UAE’s 2050 sustainability goals. Key initiatives involve marine ecosystem protection, green building, and waste management, ensuring long-term environmental resilience.
For more details, visit Umm Al Quwain’s sustainability initiatives.
Fujairah Initiatives
The Urban Observatory, an initiative by the Fujairah Municipality, plays a pivotal role in advancing the emirate’s urban sustainability strategy. This strategy aligns closely with the UAE Net Zero by 2050 strategic initiative, focusing on integrating environmental stewardship, cultural preservation, and economic growth.
Key Focus Areas of Fujairah’s Urban Observatory:
- Residential Complexes
- Green Building Projects
- Preserving Cultural Identity
- Energy Efficiency Initiatives
- Enhanced Security Measures
- Land Use and Planning
- Fujairah 2040 General Framework Project